Pregnancy brings joy and anticipation, along with health challenges. Among these, thyroid problems are prevalent. Both overactive and underactive thyroid can impact the mother and baby. If you are navigating thyroid problems during pregnancy, you are not alone. This condition affects many expectant mothers. However, we can manage these challenges with the right information and guidance.
At Nisha Women’s Hospital, Dr. Himali Maniar offers specialized care for pregnancy-related thyroid issues. She is renowned as the best gynecologist in South Bopal, Ahmedabad. Her expertise and caring nature make her a trusted choice for managing thyroid pregnancy problems during this crucial phase of life.
In this blog, we delve into thyroid issues during pregnancy. Discover insights and solutions for a healthy journey for you and your baby.
Overview of Thyroid Problems During Pregnancy
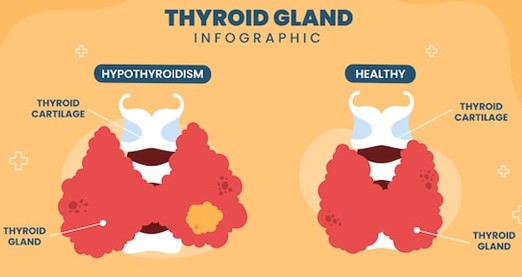
Thyroid problem during pregnancy is a significant health concern. It can affect both the mother and the developing baby. The thyroid gland is an essential part of the endocrine system. It regulates metabolism, energy, and mood.
Need expert care for your thyroid problems? Book a consultation today!
Now, let’s know the role of thyroid function in your pregnancy.
Understanding Thyroid Function in Pregnancy

The thyroid gland is small but a mighty player in the endocrine system. During pregnancy, its role expands to support the baby’s growth and brain development. It regulates metabolism and impacts both mother and baby’s health.
During pregnancy, the thyroid’s workload increases. It produces hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These are essential for fetal brain development and maintaining the mother’s metabolic rate.
About 15% of pregnant women experience changes in thyroid function. The first trimester sees a rise in Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG). It can stimulate the thyroid, sometimes lowering Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) levels. As pregnancy progresses, the body’s demand for thyroid hormones increases by about 50%.
“This change can strain an already underperforming thyroid. It can lead to conditions like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. This needs careful management to safeguard mother and child’s health,” explains Dr. Himali Maniar, a reputed gynecologist in South Bopal, Ahmedabad.
Let’s look at the different types of thyroid disorders you might encounter during pregnancy.
Types of Thyroid Disorders in Pregnancy
1. Hypothyroidism:
This condition occurs when the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones. Hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to various complications. These may include the risk of miscarriage, preterm birth, and growth issues in the baby. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, and feeling cold. Pregnant women must get regular thyroid function tests. Treatment with thyroid hormone replacement can help manage this condition.

2. Hyperthyroidism:
Hyperthyroidism happens when the thyroid gland is overactive, producing too much thyroid hormone. This condition is less common but can have a significant impact during pregnancy. It includes risks for high blood pressure and growth problems in the fetus.
Symptoms often include rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and nervousness. Treatment options include medications that reduce thyroid hormone production.

Thyroid problems in pregnancy need expert care. Don’t hesitate to book your consultation now for personalized advice and support.
Recognizing the signs is the first step to management. Let’s explore the symptoms you should watch out for.
Thyroid Symptoms During Pregnancy
In pregnancy, the presence of thyroid disorders can manifest through specific symptoms. Expectant mothers must be aware of these signs. This can help in early detection and management of the condition.
Here’s a concise rundown of critical thyroid symptoms in pregnancy:
1. Fatigue and Weakness:
While tiredness is common in pregnancy, excessive fatigue might imply a thyroid issue.
2. Weight Changes:
Unexplained weight gain or loss can be a symptom of hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
3. Mood Swings:
Severe mood changes, beyond typical pregnancy-related emotional fluctuations, could signal thyroid dysfunction.
4. Temperature Sensitivity:
A notable symptom is feeling unusually cold (hypothyroidism) or hot (hyperthyroidism).
5. Neck Swelling:
Don’t ignore noticeable swelling in the neck. It could be a sign of an enlarged thyroid gland.
6. Heart Rate Changes:
A slow (hypothyroidism) or fast (hyperthyroidism) heartbeat is often associated with thyroid issues.
7. Muscle Pain and Cramps:
These are more often associated with hypothyroidism during pregnancy.
8. Skin and Hair Changes:
Dry skin and brittle hair can be signs of an underactive thyroid. Identifying thyroid symptoms in pregnancy earlier and consulting experts like Dr. Himali Maniar, a competent lady gynecologist in South Bopal Ahmedabad, is crucial. It ensures timely and effective management of thyroid problems during pregnancy.
Here’s how to effectively manage and treat thyroid during pregnancy.
Treatment and Management Strategies

Managing thyroid disorders during pregnancy needs tailored and proactive strategies. Here’s a concise breakdown:
1. Regular Monitoring:
Close monitoring of thyroid hormone levels is crucial. Expectant mothers should often take thyroid function tests. This ensures the levels remain within a healthy range.
2. Medication Adjustment:
Your doctor may change the dosages if you are already on thyroid medication. Doctors often prescribe Levothyroxine. Its dosage is often increased during pregnancy to meet the body’s changing needs.
3. Diet and Nutrition:
Emphasizing a balanced diet rich in iodine is essential. This is because it plays a crucial role in thyroid health. Foods like dairy, fish, and iodized salt are beneficial.
4. Regular Consultations:
Regular follow-ups with specialists, including endocrinologists and obstetricians, can help manage the condition. They provide tailored advice and treatment adjustments as pregnancy progresses.
5. Postpartum Follow-up: Post-delivery thyroid levels can fluctuate. Regular monitoring and treatment changes after childbirth are crucial for long-term thyroid health.
Impact on Fetal Development and Postpartum Considerations

It is crucial to know the effect of thyroid disorders on fetal growth and postpartum health. Here’s a concise exploration:
1. Fetal Development Risks:
Thyroid disorder in the mother, especially if left untreated, can affect fetal development. Hypothyroidism can cause developmental delay and low birth weight in babies. Hyperthyroidism can lead to premature birth and a higher risk of miscarriage.
2. Neurodevelopmental Concerns:
Adequate thyroid hormone levels are essential for brain development in fetus. Imbalances can result in cognitive and developmental challenges for the child. This emphasizes the importance of monitoring and managing thyroid health during pregnancy.
3. Postpartum Thyroiditis:
Postpartum thyroiditis, a thyroid gland inflammation, often occurs after delivery. This condition can present as hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or both sequentially. It impacts new mothers’ health and well-being.
4. Long-term Health of Mother and Child:
Proper management of thyroid disorders during pregnancy safeguards the mother’s health. It also sets a foundation for the child’s long-term well-being. Regular monitoring and treatment adjustments are crucial to ensuring optimal outcomes for both.
Conclusion
Managing thyroid problems during pregnancy is critical. It helps safeguard the health and well-being of both mother and baby. Expectant mothers with thyroid disorders should consult specialists like Dr. Himali Maniar. She is a highly qualified and skilled lady gynecologist in Bopal Ahmedabad. Dr. Himali offers personalized care tailored to patient’s needs. With expert guidance and attentive care, a healthy pregnancy is an achievable reality.
Get the clarity you need. Arrange a consultation with our specialists to discuss your thyroid health during pregnancy.
Have questions? Let’s address some common concerns.
FAQs:
Can thyroid problems affect the baby during pregnancy?
Yes, thyroid issues can impact your baby’s health. An underactive or overactive thyroid in pregnancy can lead to various complications. These may include preterm birth or low birth weight. Proper management of these conditions is vital for your and your baby’s health.
What are the thyroid symptoms in pregnancy?
If you are pregnant with a thyroid condition, you may experience various symptoms. It may include fatigue, weight changes, or mood swings. These can be like regular pregnancy symptoms. Hence, monitoring your thyroid levels for any significant changes is essential.
What should I do if I have symptoms of a thyroid disorder while pregnant?
If you suspect a thyroid issue during pregnancy, contact your healthcare provider. They will recommend blood tests to check your thyroid hormone levels. After diagnosis, they can adjust your treatment plan to keep you and your baby healthy.
How can I control my thyroid during pregnancy?
Managing your thyroid during pregnancy often involves regular monitoring and medication adjustments. Your doctor will guide you on the right dosage and frequency of medication. They can also suggest lifestyle changes to help control your thyroid levels. These may include a balanced diet and stress management.
Can a woman with thyroid problems get pregnant?
Women with thyroid issues can become pregnant. Managing thyroid levels before and during pregnancy is essential to reduce complications. Regular check-ups and a tailored treatment can help maintain a healthy pregnancy.
Reference links:

